Laparoscopic Hiatus Hernia Repair by Hernia Specialist – Dr. Mohit Agrawal
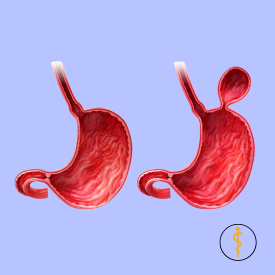
When it comes to treating appendicitis, choosing an experienced surgeon is crucial. Dr. Mohit Agrawal, a leading laparoscopic surgeon, offers expert care and advanced surgical techniques for performing laparoscopic hiatus hernia. A hiatus hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach bulges through an opening in the diaphragm into the chest. The diaphragm is a muscle, located between the abdomen and chest, has a small opening called the hiatus where the esophagus passes from the chest to connect with the stomach in the abdomen. When a portion of the stomach pushes through this opening, a hiatus hernia is formed.
This is the most common type of hiatal hernia. It occurs when the stomach and esophagus slide in and out of the chest through the hiatus. These hernias are generally small and often don’t cause any symptoms.
This type is rarer and occurs when part of the stomach becomes stuck in the diaphragm. While often not severe, there’s a risk of blood supply being cut off to the stomach, creating a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
(Combination of the above)
Common symptoms include:
Immediate medical attention is needed if you experience severe chest or belly pain, inability to pass stool or gas, or persistent stomach upset.
Hiatal hernias typically result from a weakened diaphragm muscle that allows part of the stomach to push through. Common causes include:
Tests for diagnosis include:
While there are no medications to treat the hernia itself, doctors may prescribe antacids, acid-blocking medications, and proton pump inhibitors to relieve symptoms
This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions in the abdomen. A laparoscope is inserted to view and repair the hernia. A mesh may be used to tighten the hiatus and prevent recurrence.
In this procedure, the upper portion of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus to reinforce the hiatus and prevent acid reflux.
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing a hiatal hernia include:
While you can’t prevent a hiatal hernia entirely, you can manage symptoms and reduce the risk of acid reflux by:
In some cases, hiatal hernias can lead to:
Dr. Mohit Agrawal is one of the best doctor for diagnosis and treatment of hiatal hernias in Goregaon, Kandivali, Borivali & Malad. With years of experience in laparoscopic and robotic surgery, he ensures precision and safety in every procedure, offering patients the best possible outcomes.
Laparoscopic hiatus hernia repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to treat a hiatus hernia, where part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. The surgery involves repairing the hernia and strengthening the diaphragm to prevent recurrence.
The benefits include:
1) Smaller incisions
2) Reduced postoperative pain
3) Faster recovery time
4) Minimal scarring
5) Shorter hospital stay
This procedure is recommended for patients who:
1) Have severe or persistent symptoms such as acid reflux, chest pain, or difficulty swallowing.
2) Have not responded to medication or lifestyle changes.
3) Have complications like a large hernia or esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus).
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen, inserts a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera), and uses specialized instruments to repair the hernia. The stomach is repositioned, and the opening in the diaphragm is tightened with sutures.
Laparoscopic hiatus hernia repair typically takes 1-2 hours, depending on the case’s complexity.
Patients usually:
1) Stay in the hospital for 1-2 days.
2) Resume light activities within a week.
3) Follow a special diet for the first few weeks, gradually transitioning to normal food.
4) Return to normal activities within 2-4 weeks.
While laparoscopic hiatus hernia repair is generally safe, potential risks include:
1) Infection or bleeding
2) Difficulty swallowing (temporary)
3) Recurrence of the hernia
4) Adverse reactions to anesthesia
The procedure has a high success rate, with most patients experiencing significant relief from symptoms and improved quality of life.
Your doctor may recommend:
1) Fasting for a certain period before surgery.
2) Avoiding certain medications like blood thinners.
3) Completing preoperative tests, such as blood or imaging studies.
The cost can vary based on factors like the hospital, the surgeon’s expertise, and the complexity of the case. On average, the cost ranges from ₹1,50,000 to ₹3,00,000.
Most health insurance policies cover laparoscopic hiatus hernia repair if deemed medically necessary. Check with your insurance provider for specific details.
Mumbai is home to some of the best laparoscopic surgeons and advanced healthcare facilities in India. You can expect:
1) Experienced surgeons specializing in minimally invasive procedures.
2) World-class hospitals equipped with state-of-the-art technology.
3) Comprehensive pre- and post-operative care.
Laparoscopic hiatus hernia repair is a minimally invasive procedure to treat a hiatus hernia, where part of the stomach moves into the chest cavity through the diaphragm. It is performed to reduce symptoms like acid reflux, heartburn, and chest pain and to prevent complications such as esophagitis or strangulation of the hernia.
Mumbai offers access to experienced laparoscopic surgeons, modern medical facilities, and advanced technology. The laparoscopic approach ensures smaller incisions, faster recovery, minimal scarring, and a shorter hospital stay, all while providing world-class care at affordable costs.
Most patients recover quickly after laparoscopic surgery. Light activities can be resumed within a week and normal activities typically within 2-4 weeks. Patients need to follow a soft diet initially and gradually transition to regular food as advised by their doctor.
Ready to take the next step towards expert and personalized care for Laparoscopic Hiatus Hernia Repair by Hernia Specialist – Dr. Mohit Agrawal?
Contact us today to schedule your consultation. Our experienced Laparoscopic Hiatus Hernia Repair by Hernia Specialist – Dr. Mohit Agrawal team is here to provide expert guidance and ensure your comfort throughout the process.