Diabetic foot
Individuals with diabetes face a heightened risk of foot complications, particularly if they experience diabetes-related neuropathy or poor blood circulation. Diabetes-related neuropathy occurs when nerve damage results from consistently high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia), with the feet often being the most affected area.
The progression of foot complications in diabetic patients can follow a concerning chain of events:
Given these risks, diligent foot care and effective diabetes management are critical. Simple preventive measures can help minimize foot issues.
Any skin, nerve, or circulation problem affecting the feet can escalate into serious complications for those with diabetes. Common foot and toe conditions that may arise include:
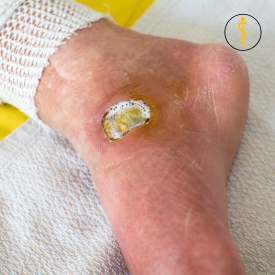
Foot and toe ulcers, or open sores, are prevalent among those with diabetes, affecting approximately 15% of individuals. These ulcers often develop in areas where repeated friction occurs, such as from ill-fitting shoes.
Ulcers can lead to infections, and in severe cases, the infection may require surgical intervention, including amputation. Early detection and treatment are crucial to minimizing the risk of amputation.
Be vigilant for the following symptoms indicative of diabetes-related foot conditions:
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Serious complications from diabetes-related foot conditions include:
Untreated foot infections can lead to gangrene, a critical medical emergency where blood flow ceases to a specific body area, causing tissue death. Symptoms of gangrene include:
Seek immediate medical assistance if you observe signs of gangrene.
A rare complication of diabetes-related neuropathy, Charcot foot can lead to joint collapse and permanent loss of foot function if untreated. Early signs include:
If you notice these symptoms, consult your healthcare provider promptly.
The primary causes of diabetes-related foot conditions are:
Maintaining high blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels, increasing the likelihood of neuropathy and PAD. Proper foot care, such as avoiding ill-fitting shoes and regularly inspecting feet, can further reduce the risk of complications.
A healthcare provider will diagnose diabetes-related foot conditions through:
Treatment varies based on the specific condition and may involve a podiatrist specializing in foot care. Common interventions include:
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes-related foot conditions:
Diabetes-related foot conditions are common but can lead to serious complications if not managed properly. Early detection and treatment are vital. If you notice any concerning symptoms, please consult Dr. Mohit Agrawal to discuss your foot health and appropriate preventive measures. Maintaining foot health is an essential aspect of diabetes care. For further information or to schedule an appointment, contact Dr. Mohit Agrawal today.
A diabetic foot is a complication of diabetes where high blood sugar levels cause nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor blood circulation, leading to foot ulcers, infections, or even gangrene if untreated.
Symptoms include:
1) Foot pain or numbness
2) Swelling and redness
3) Open sores or ulcers that do not heal
4) Foul-smelling discharge from wounds
5) Blackened or dead tissue (gangrene)
They are caused by:
1) Poor blood circulation (peripheral arterial disease)
2) Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy)
3) High blood sugar levels that delay wound healing
4) Foot injuries or infections that go unnoticed due to loss of sensation
Yes, by managing blood sugar levels, maintaining proper foot hygiene, wearing comfortable footwear, and regularly checking for any injuries or changes in the feet.
Diagnosis involves:
1) Physical examination of the feet
2) Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to assess bone and tissue damage
3) Doppler studies or angiography to check blood circulation
4) Blood tests to identify infections or elevated sugar levels
Treatment depends on the severity and may include:
1) Antibiotics for infections
2) Wound care and dressings
3) Debridement (removal of dead tissue)
4) Surgery for severe cases (e.g., drainage, reconstruction, or amputation in extreme cases)
Common surgical procedures include:
1) Debridement: Removing dead or infected tissue
2) Incision and drainage: To treat abscesses
3) Vascular surgery: To improve blood flow
4) Amputation: In severe cases to prevent the spread of infection
No, surgery is only required for severe cases, such as persistent infections, abscesses, gangrene, or when conservative treatments fail.
Yes, advanced treatments include:
1) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) to improve healing
2) Laser treatments for blood flow enhancement
3) Skin grafting for severe ulcers
4) Advanced wound care techniques using growth factors or stem cells
Recovery time varies based on the type of surgery and the patient’s overall health. Minor surgeries may take 1-2 weeks to heal, while major procedures like amputation may take several weeks to months for complete recovery.
Surgery addresses specific complications, such as infections or ulcers, but managing diabetes and maintaining proper foot care is essential to prevent recurrence.
Post-treatment care includes:
1) Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels
2) Proper wound care and dressing changes
3) Wearing specially designed diabetic footwear
4) Avoiding injuries or pressure on the treated foot
While surgery is generally safe, potential risks include:
1) Infection at the surgical site
2) Delayed wound healing
3) Blood clots or poor circulation
4) Need for further surgeries in severe cases
The cost depends on the severity and treatment required:
1) Basic wound care: ₹5,000 to ₹15,000
2) Minor surgery (debridement): ₹20,000 to ₹50,000
3) Major surgery (e.g., vascular reconstruction or amputation): ₹50,000 to ₹2,00,000
Most health insurance policies cover diabetic foot surgeries and treatments if they are medically necessary. However, coverage may vary, so it is best to check with your provider.
Mumbai offers some of the best diabetic foot specialists, advanced medical facilities, and access to cutting-edge treatments like laser therapy and HBOT. The city also provides high-quality care at competitive prices, making it a top choice for diabetic foot management.
Ready to take the next step towards expert and personalized care for Diabetic foot?
Contact us today to schedule your consultation. Our experienced Diabetic foot team is here to provide expert guidance and ensure your comfort throughout the process.